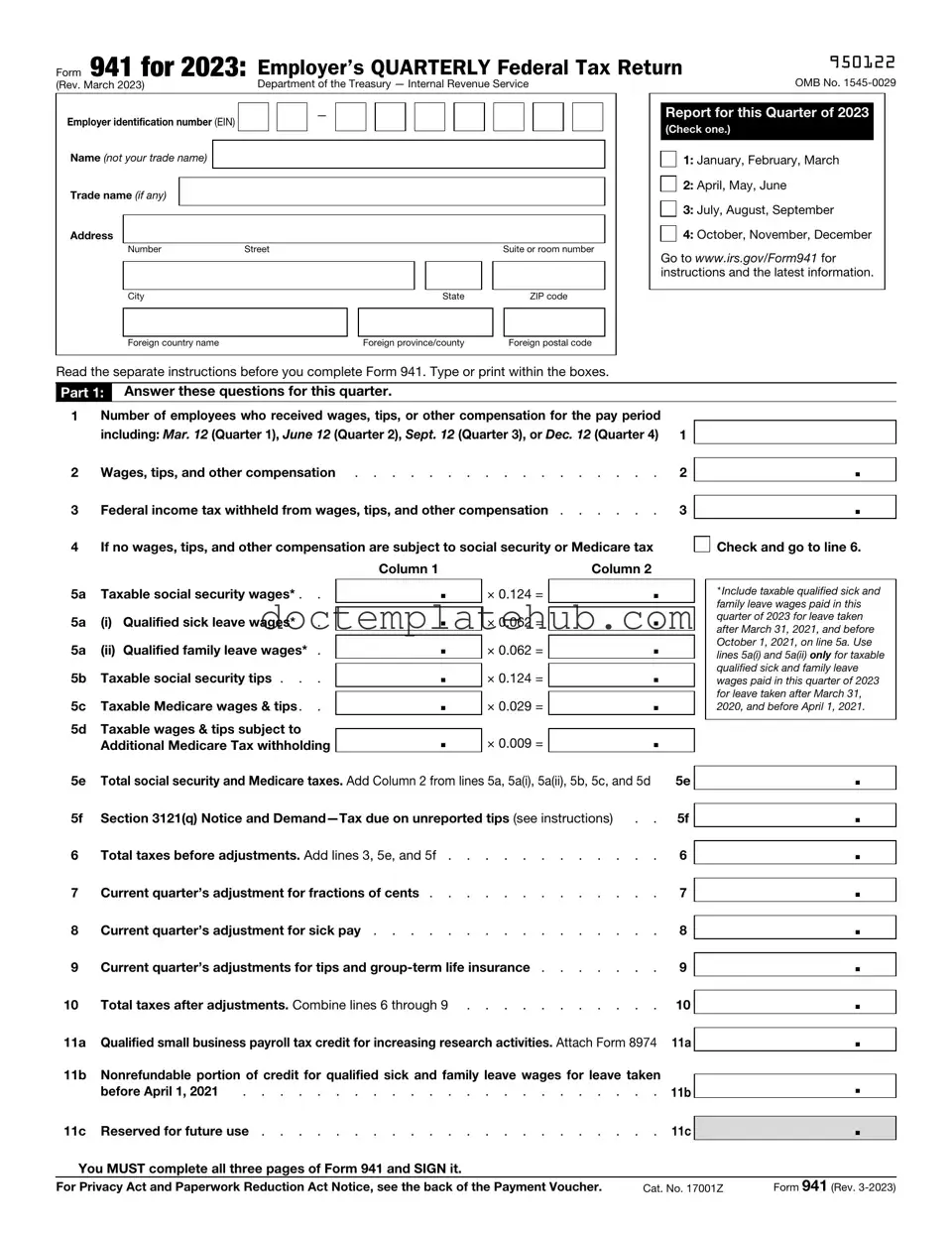
Fill Your IRS 941 Form
The IRS Form 941, also known as the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, plays a crucial role in the tax obligations of employers across the United States. This form is filed quarterly and is used to report income taxes, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax withheld from employees' paychecks. Employers must also account for their portion of Social Security and Medicare taxes, making this form essential for accurate payroll reporting. By submitting Form 941, employers provide the IRS with important information about their tax liabilities and payments for each quarter, ensuring compliance with federal tax laws. Additionally, the form includes sections for reporting adjustments, which may arise from various circumstances such as corrections to previous filings or changes in employee status. Understanding the requirements and deadlines associated with Form 941 is vital for employers to avoid penalties and maintain good standing with the IRS. With the right information and careful attention to detail, employers can navigate this process smoothly, fulfilling their responsibilities while supporting their workforce effectively.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 940 is similar to Form 941 in that both are used by employers to report taxes related to employee wages. While Form 941 focuses on quarterly payroll taxes, including federal income tax withholding and Social Security and Medicare taxes, Form 940 is an annual report of the Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) tax. Employers use Form 940 to report and pay unemployment taxes, which help fund unemployment benefits for workers who lose their jobs. Both forms require accurate reporting of wages and taxes, ensuring compliance with federal tax regulations.
Form W-2, the Wage and Tax Statement, is another document closely related to Form 941. Employers must issue Form W-2 to each employee by the end of January following the tax year. This form details the total wages paid and the taxes withheld, including federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes. While Form 941 is a summary of these amounts on a quarterly basis, Form W-2 provides a comprehensive view for each employee's annual earnings and tax contributions, facilitating individual tax filing.
Form 1099-MISC serves a similar purpose but is designed for independent contractors and non-employees. Employers use this form to report payments made to individuals who are not classified as employees. Like Form 941, which tracks employee wages and withholdings, Form 1099-MISC captures payments made to freelancers or service providers. Both forms help the IRS ensure that all income is reported and taxed appropriately, maintaining the integrity of the tax system.
Form 944 is another variant that shares similarities with Form 941. Designed for smaller employers, Form 944 allows eligible businesses to file their payroll taxes annually instead of quarterly. This form simplifies the reporting process for those with a lower payroll tax liability. While Form 941 requires quarterly submissions, Form 944 consolidates that information into one annual report, reducing the frequency of filing while still ensuring compliance with federal tax obligations.
Form 945 is relevant for employers who make non-payroll payments, such as backup withholding. This form is used to report federal income tax withheld from payments made to non-employees. Like Form 941, which reports payroll taxes, Form 945 ensures that the IRS receives accurate information regarding tax withholdings. Both forms are essential for maintaining transparency in tax reporting and ensuring that the appropriate taxes are collected and remitted to the government.
For those interested in understanding the financial obligations involved, a practical guide to a Georgia Promissory Note is essential for navigating loan agreements effectively. You can access more information by visiting this link.
Finally, Form 1065, the U.S. Return of Partnership Income, also bears similarities to Form 941 in that it is used to report income and expenses for partnerships. While Form 941 is focused on payroll taxes for employees, Form 1065 reports the income, deductions, gains, and losses of a partnership. Both forms are crucial for tax compliance, ensuring that the IRS has a clear picture of income and tax liabilities, whether from employee wages or partnership earnings.
Other PDF Templates
Seating Chart Generator Band - Follow the seating chart for the traditional setup.
In order to ensure the highest level of confidentiality when dealing with sensitive information, it is crucial to utilize a well-drafted legal framework. For those in Michigan, a Michigan Non-disclosure Agreement is indispensable, as it safeguards proprietary information and trade secrets. To learn more about how to create a robust agreement, you can visit smarttemplates.net, where you'll find useful templates and resources to assist you in this process.
Act of Donation Louisiana Pdf - Utilizing this form is critical for a successful and lawful property transfer.
Florida Immunization Records - Healthcare providers can assist in completing the form and understanding its implications.
More About IRS 941
What is IRS Form 941?
IRS Form 941 is a quarterly tax form that employers use to report income taxes, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax withheld from employees' paychecks. It also helps report the employer's share of Social Security and Medicare taxes. This form is essential for the IRS to track employment taxes and ensure compliance.
Who needs to file Form 941?
Any business that pays wages to employees must file Form 941. This includes corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. If you have employees, you are required to file this form quarterly, even if you did not withhold any taxes during that period.
When is Form 941 due?
Form 941 is due on the last day of the month following the end of each quarter. For example, for the first quarter (January to March), the due date is April 30. For the second quarter (April to June), it is July 31. The third quarter (July to September) is due on October 31, and the fourth quarter (October to December) is due on January 31 of the following year.
What happens if I miss the deadline for filing Form 941?
If you miss the deadline, you may face penalties and interest on any unpaid taxes. The IRS can charge a late filing penalty, which can be significant. It’s crucial to file on time to avoid these additional costs.
Can I amend a previously filed Form 941?
Yes, you can amend a previously filed Form 941 by using Form 941-X, Adjusted Employer’s QUARTERLY Federal Tax Return or Claim for Refund. This form allows you to correct errors or make adjustments to your original filing. Be sure to file it as soon as you realize a mistake to minimize any potential penalties.
What information do I need to complete Form 941?
You will need your employer identification number (EIN), the number of employees, total wages paid, and the amount of taxes withheld. Additionally, you should have records of any adjustments for tax credits or overpayments. Keeping accurate records will make the process smoother.
Is there an electronic filing option for Form 941?
Yes, you can file Form 941 electronically through the IRS e-file system or through authorized e-file providers. Electronic filing is often faster and more efficient than paper filing. It also helps reduce the risk of errors and ensures that your form is processed more quickly.
What should I do if I have no employees during a quarter?
If you have no employees during a quarter, you still need to file Form 941. You should indicate that there were no wages paid and no taxes withheld. This keeps your filing status current and informs the IRS that your business is still active.
Where can I find help if I have questions about Form 941?
If you have questions about Form 941, you can visit the IRS website for detailed instructions and resources. Additionally, consider consulting a tax professional or accountant for personalized guidance. They can provide assistance tailored to your specific situation.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS 941 form, it's important to follow certain guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here’s a list of things you should and shouldn't do:
- Do double-check your employer identification number (EIN) for accuracy.
- Don't forget to report all wages paid to employees.
- Do include any adjustments for sick pay or tips.
- Don't leave any required fields blank; fill in all necessary information.
- Do verify your calculations for accuracy before submitting.
- Don't submit the form late; adhere to the deadlines.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Don't use pencil; always fill out the form in ink or electronically.
- Do seek assistance if you're unsure about any part of the form.
Following these guidelines can help you avoid common mistakes and ensure a smoother filing process.
IRS 941 - Usage Steps
Filling out the IRS Form 941 is an important task for employers who need to report payroll taxes. After completing the form, you will submit it to the IRS, which helps ensure compliance with federal tax obligations. Follow these steps carefully to fill out the form accurately.
- Gather necessary information, including your Employer Identification Number (EIN), business name, and address.
- Begin with the top section of the form. Fill in your EIN, business name, and address in the designated fields.
- Indicate the quarter for which you are filing. The quarters are January-March, April-June, July-September, and October-December.
- In the next section, report the number of employees you had during the quarter.
- Calculate the total wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees during the quarter. Enter this amount in the appropriate box.
- Determine the total taxes withheld from employees' paychecks. This includes federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
- Fill out any adjustments for tips and group-term life insurance, if applicable.
- Calculate the total taxes due for the quarter by summing the amounts from previous sections.
- Complete the section for any deposits made during the quarter. This includes any amounts you have already paid to the IRS.
- Finally, sign and date the form. Ensure that you provide your title if you are signing on behalf of the business.
After completing these steps, review the form for accuracy. Make sure all calculations are correct and that you have included all necessary information. Once you’re confident everything is in order, submit the form to the IRS by the due date to avoid any penalties.